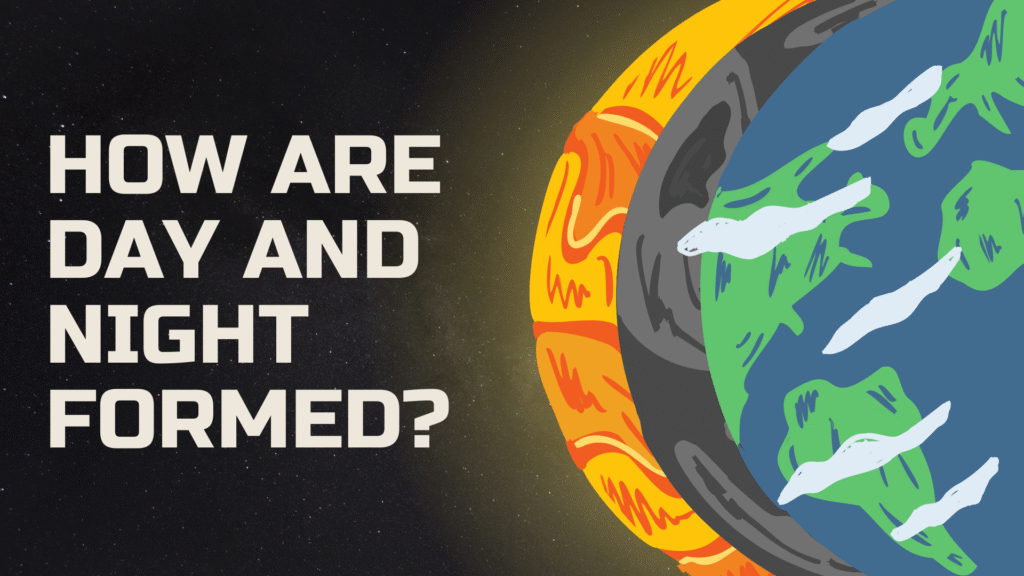
How Are Day and Night Formed Based on Earth’s Rotation?
The Earth has many astonishing and fascinating phenomena, such as rainbows, the twinkling of stars, volcanic eruptions, rainfall, snowfall, and many more. One such interesting phenomenon is the occurrence of day and night and the cosmic changes that make this happen. In this article, we will explain how are day and night formed. You will learn about the day-night cycle and other interesting concepts, such as equinoxes, solstices, the midnight sun, and polar nights.
What causes day and night?
Day and night occur because of the rotation of the Earth. The Earth takes approximately 24 hours to complete one rotation (or spin) around its axis. The part of the Earth that faces the sun experiences day, while the part that is away from the sun experiences night.
As Earth keeps rotating, different places experience day and night at different times. Here are some more interesting concepts related to day and night for kids:
1. Equinox
Equinox is the time or date when the Sun is directly over the Equator. At this position, neither of the two hemispheres are tilted more towards the Sun than the other keeping them both at an equidistance. As a result, the Sun’s rays fall directly over the middle of the Earth, and both the Northern and Southern Hemispheres receive equal sunlight. On an equinox, the entire planet experiences equal day and night.
Equinox happens twice every year, once on March 21 and September 23. The March equinox marks the beginning of spring, and the September equinox marks the beginning of autumn.
2. Solstice
Solstices occur when the Earth’s tilt makes the Sun appear farthest north or south of the Equator. Solstices happen twice a year, once on June 21 and then on December 21.
In the Northern Hemisphere, the June solstice is called the Summer solstice. It causes the longest day and shortest night. The December solstice is called the Winter solstice. It causes the shortest day and longest night.
3. Seasons
Seasons occur because the Earth’s axis is tilted at 23.5 degrees. Due to this tilt, different parts of the Earth receive different amounts of sunlight during the year.
When a part of the Earth is tilted towards the Sun, it experiences the summer season with longer days and shorter nights. When it is tilted away from the Sun, it experiences winter. In winter, the days become shorter and the nights become longer.
During the spring and autumn seasons (equinox), the Sun is directly over the Equator. On these days, both hemispheres receive equal sunlight, making the days and nights are equal all over the Earth.
4. Midnight Sun
The Midnight Sun is a special phenomenon in which the sun can be seen even at midnight in places near the North and South Poles.
It happens because the Earth is tilted at 23.5 degrees. During the summer season, a part of our planet is tilted towards the Sun. In the places near the poles, the sun does not go below the horizon, so it stays bright all day and all night.
The Midnight Sun occurs near the Arctic Circle in the Northern Hemisphere and the Antarctic Circle in the Southern Hemisphere.
5. Polar Night
Polar Night is the time when the Sun does not rise for many days. This also happens due to the Earth’s tilt. During the winter season, a part of the Earth is tilted away from the Sun. Near the poles, the Sun stays below the horizon, so it remains dark all day. It can last for several days, weeks, and months, depending on how close the place is to the pole.
The Polar night occurs near the Arctic Circle in the Northern Hemisphere and the Antarctic Circle in the Southern Hemisphere.
The bottom line
The formation of day and night depends on Earth’s rotation on its axis. As the Earth rotates, different parts of the planet face the sun, causing days (a period of light). The parts away from the Sun experience nights (a period of darkness).
As the Earth takes 24 hours to complete one full rotation, each part of the Earth experiences both day and night once. However, North Pole and South Pole are exceptions due to the geography. They roughly experience sunshine for six months and darkness for the remaining six months.
Frequently asked questions
1. How are day and night formed?
Day and night are formed when the Earth rotates on its axis. The part of the Earth that faces the Sun during the rotation experiences day, while the part that is away from the Sun experiences night.
2. How long does one day take?
One complete rotation of the Earth takes 24 hours.
3. Does the sun move to cause day and night?
No, the Earth moves to cause day and night.
4. Why is it day in some places and night in others?
Different parts of Earth face the sun at various times. The part facing the Sun has day, while the other part has night.
5. Can we see the Moon during the day?
Yes, we can see the Moon during the day. The Moon reflects sunlight, so it can sometimes be seen in the daytime.
6. Why are days longer in summer?
Days are longer in summer because the Earth is tilted towards the sun.
7. Why do we see stars only during the night?
Stars are present in the sky during the day, too, but the brightness of the sun hides them during the day.
8. Why are nights longer in winter?
Nights are longer in winter because the Earth is tilted away from the sun during that time.
9. What is an equinox?
An equinox is a day when day and night are equal all over the Earth.
10. What is a solstice?
A solstice is a day when the day is either the longest or the shortest of the year. It happens twice a year due to Earth’s tilt.
11. What is the Midnight Sun?
The Midnight Sun is when the Sun is visible even at midnight. It happens in places near the poles.
12. What is Polar Night?
Polar Night is when the Sun does not rise for many days. It happens in places near the poles.